
 Point elasticity: The measure of the change in quantity demanded to a very small change in price. To calculate the point elasticity, you must have a function for the relationship between price and quantity. The point elasticity captures the change in quantity demanded to a tiny change in price. You do not need to know the function relating price and quantity demanded to use this method. The midpoint method can be used if just two points on the demand curve are known. The arc elasticity captures the responsiveness of one variable to another between two given points. When changes in price and quantity are big, the arc elasticity or point elasticity formulas provide a more accurate elasticity coefficient than the basic elasticity formula. The consumer may be selecting more luxurious substitutes as a result of the increase in income. This is an inferior good (all other goods are normal goods). Negative income elasticity of demand (YED<0): An increase in income is accompanied by a decrease in the quantity demanded. Zero income elasticity of demand (YED=0): A change in income has no effect on the quantity bought. This is characteristic of a necessary good. Low income elasticity of demand (YED<1): An increase in income is accompanied by less than a proportional increase in quantity demanded. Unitary income elasticity of demand (YED=1): An increase in income is accompanied by a proportional increase in quantity demanded. This is typical of a luxury or superior good. High income elasticity of demand (YED>1): An increase in income is accompanied by a proportionally larger increase in quantity demanded. Income Elasticity of Demand: Income elasticity of demand measures the percentage change in quantity demanded as income changes. Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand (E A,B) is calculated with the following formula: More specifically, it captures the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of one good to a change in price of another good. The cross-price elasticity of demand shows the relationship between two goods or services. substitute: A good with a positive cross elasticity of demand, meaning the good's demand is increased when the price of another is increased. Complement: A good with a negative cross elasticity of demand, meaning the good's demand is increased when the price of another good is decreased. Independent goods have a cross-price elasticity of zero: as the price of one good increases, the demand for the second good is unchanged. Substitute goods have a positive cross-price elasticity: as the price of one good increases, the demand for the other good increases.
Point elasticity: The measure of the change in quantity demanded to a very small change in price. To calculate the point elasticity, you must have a function for the relationship between price and quantity. The point elasticity captures the change in quantity demanded to a tiny change in price. You do not need to know the function relating price and quantity demanded to use this method. The midpoint method can be used if just two points on the demand curve are known. The arc elasticity captures the responsiveness of one variable to another between two given points. When changes in price and quantity are big, the arc elasticity or point elasticity formulas provide a more accurate elasticity coefficient than the basic elasticity formula. The consumer may be selecting more luxurious substitutes as a result of the increase in income. This is an inferior good (all other goods are normal goods). Negative income elasticity of demand (YED<0): An increase in income is accompanied by a decrease in the quantity demanded. Zero income elasticity of demand (YED=0): A change in income has no effect on the quantity bought. This is characteristic of a necessary good. Low income elasticity of demand (YED<1): An increase in income is accompanied by less than a proportional increase in quantity demanded. Unitary income elasticity of demand (YED=1): An increase in income is accompanied by a proportional increase in quantity demanded. This is typical of a luxury or superior good. High income elasticity of demand (YED>1): An increase in income is accompanied by a proportionally larger increase in quantity demanded. Income Elasticity of Demand: Income elasticity of demand measures the percentage change in quantity demanded as income changes. Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand (E A,B) is calculated with the following formula: More specifically, it captures the responsiveness of the quantity demanded of one good to a change in price of another good. The cross-price elasticity of demand shows the relationship between two goods or services. substitute: A good with a positive cross elasticity of demand, meaning the good's demand is increased when the price of another is increased. Complement: A good with a negative cross elasticity of demand, meaning the good's demand is increased when the price of another good is decreased. Independent goods have a cross-price elasticity of zero: as the price of one good increases, the demand for the second good is unchanged. Substitute goods have a positive cross-price elasticity: as the price of one good increases, the demand for the other good increases. 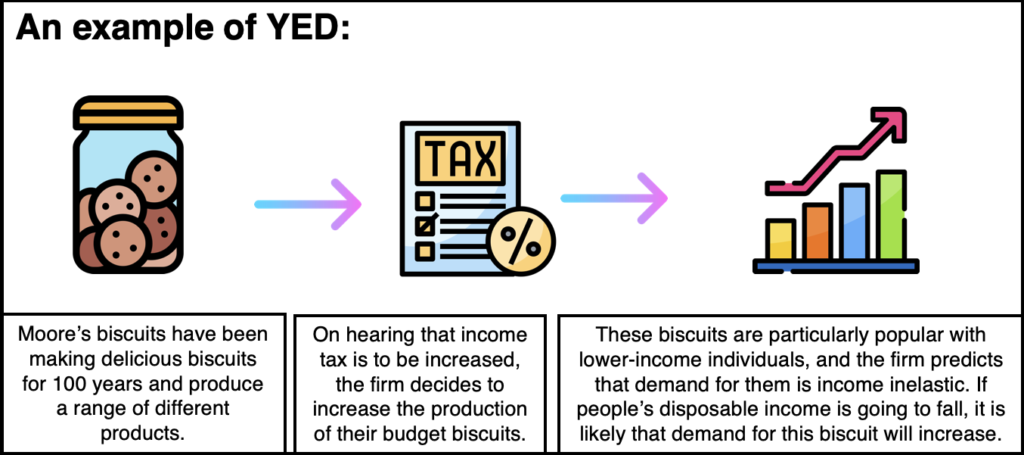
Complementary goods have a negative cross- price elasticity: as the price of one good increases, the demand for the second good decreases.
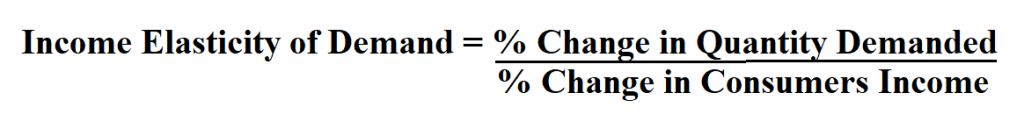

Fine wines and spirits, high quality chocolates (e.g.The income elasticity of demand is usually strongly positive for Examples include the demand for cigarettes, low-priced own label foods in supermarkets and the demand for council-owned properties. Typically inferior goods or services tend to exist where superior goods are available if the consumer has the money to be able to buy it. However, there are some products (economists call them "inferior goods") which have a negative income elasticity of demand, meaning that demand falls as income rises. The income elasticity of demand in this example is +1.25. demand rises more than proportionate to a change in income – for example a 8% increase in income might lead to a 10% rise in the demand for restaurant meals. Luxury goods and services have an income elasticity of demand > +1 i.e. Demand is rising less than proportionately to income.Ģ. Normal necessities have an income elasticity of demand of between 0 and +1 for example, if income increases by 10% and the demand for fresh fruit increases by 4% then the income elasticity is +0.4. So as consumers' income rises more is demanded at each price.ġ. Most products have a positive income elasticity of demand. % change in demand divided by the % change in income The formula for calculating income elasticity is: Income elasticity of demand measures the relationship between a change in quantity demanded for good X and a change in real income. This leads onto another important elasticity – the income elasticity of demand (often shortened to Yed). However, it is also affect by the incomes of consumers. The amount that customers demand is affected by price (Ped).




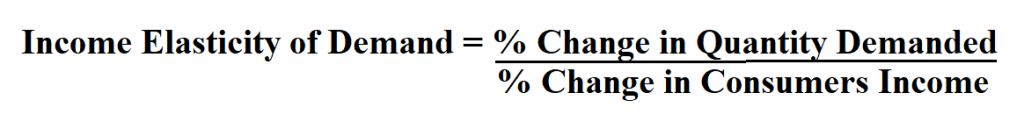



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
